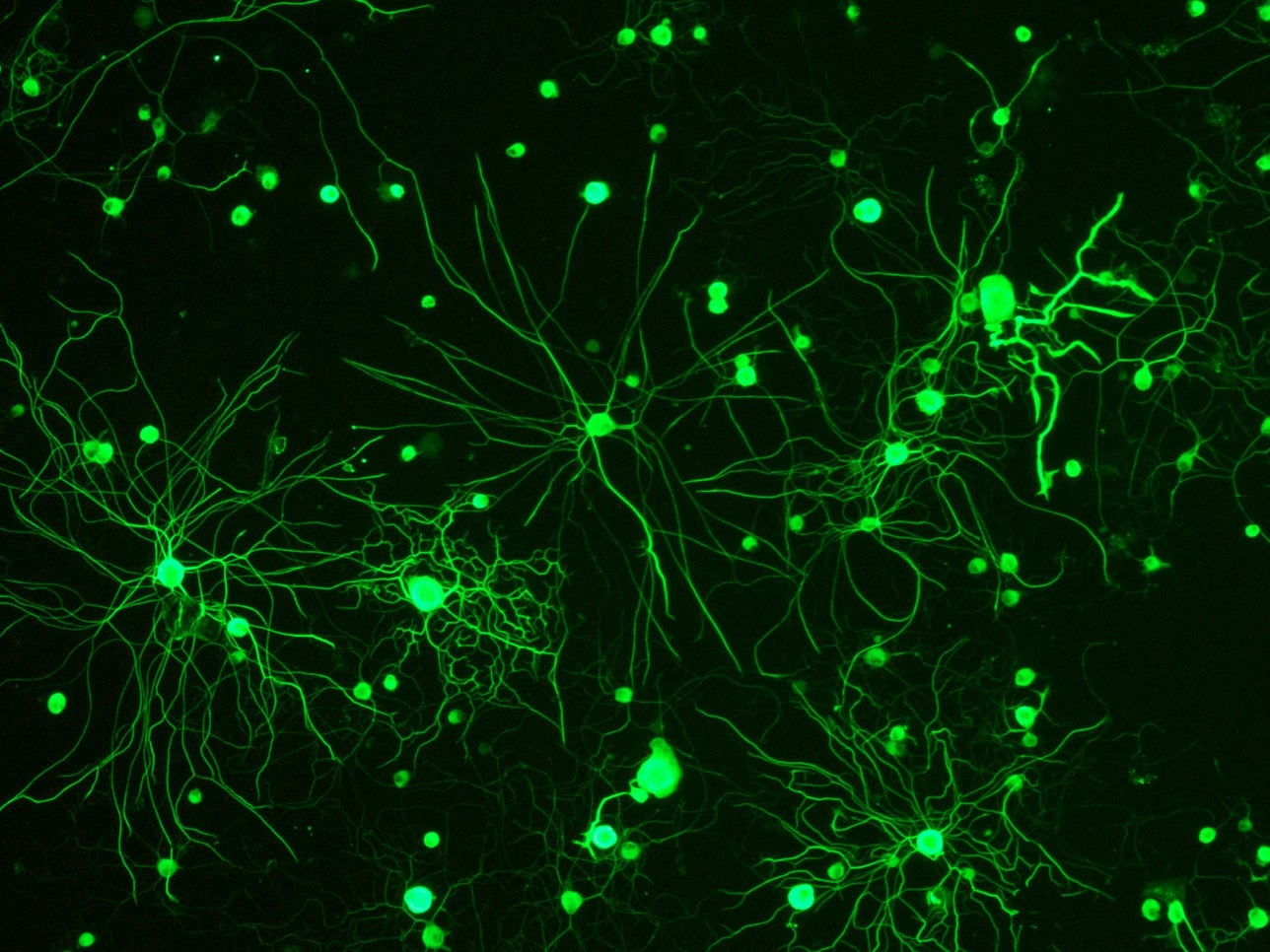
Is the study of the nervous system. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches, such as optogenetics, a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by the expression of light-sensitive ion channels, pumps, or enzymes specifically in the target cells.

In the fields of neurobiology and optogenetics, microscopes are used to study the intricate structures and processes of the nervous system. They enable visualization of individual neurons, cellular dynamics, and neural activity.
Various microscopy techniques provide insights into neuronal morphology, protein localization, and the effects of optogenetic manipulation. Through detailed observations, microscopes contribute to advancing our understanding of brain function and neurological disorders.
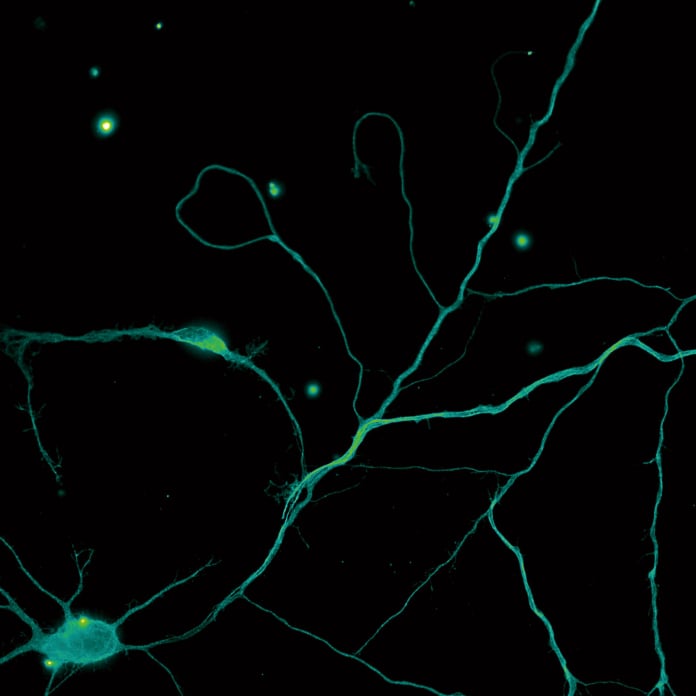
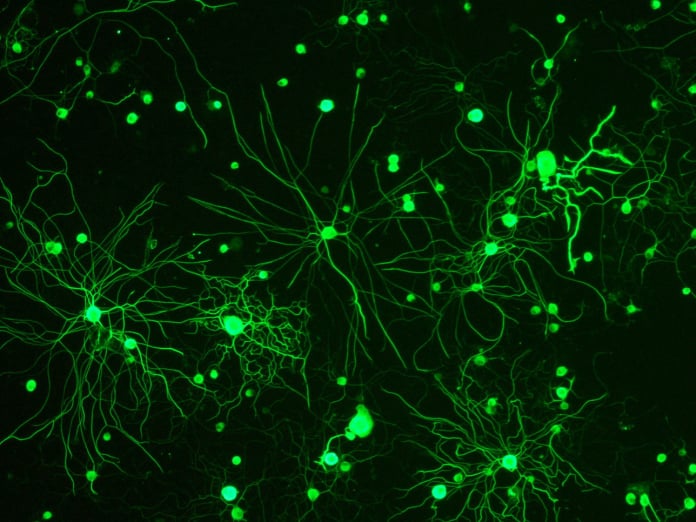
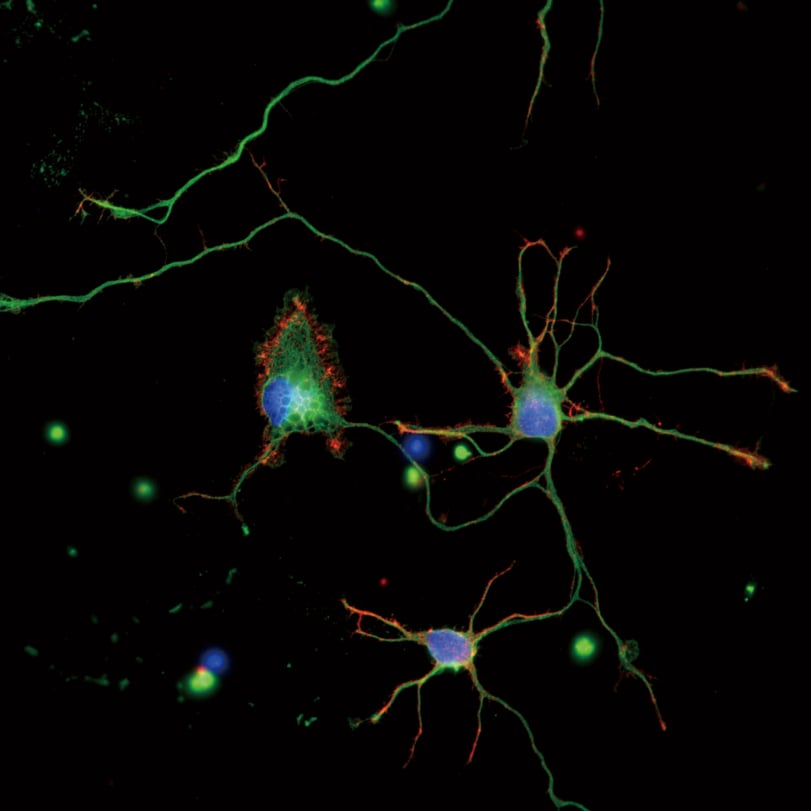

The structure of a neuromuscular junction in a mouse captured by high-definition 3D imaging using a resonant scanner.
Keywords: high-speed XY-Z, high resolution, large FOV

Nerve endings adhering to muscle cells. The white arrows indicate the distribution of acetylcholine receptors (red) surrounding the neurons (green)
DAPI: cell nucleus (blue), GFP: neurons (green), Alexa 555: acetylcholine receptor (red), CMDR: cell membrane (gray)
Objective: CFI Plan Apochromat Lambda S 25xC Sil

Entire view of mouse muscle tissue. Using a resonant scanner, 6 images were tiled during Z-stack imaging. Image resolution: 1024 x 1024 pixels. MIP display of captured Z-stack images. Objective: CFI Plan Apochromat Lambda 10X
Since a resonant scanner can perform confocal imaging with higher temporal resolution than a Galvano scanner, it is used in many cases to acquire life phenomena occurring at high speeds. In contrast, because the resonant scanner of the new generation AX R confocal microscope system supports up to 2K x 2K acquisition, it can be used for a wide range of purposes, from high-speed imaging to high-resolution imaging. Learn More...



*Photos courtesy of Nikon official website
Designed with Mobirise web page themes